Purdue launches quantum supercomputing center
Purdue University during a two-day international workshop beginning Oct. 13 will launch a new center dedicated to quantum science and technology, which could bring advances rivaling those from integrated circuits and lasers.
The university will announce the Purdue Quantum Center during the International Workshop on Quantum Control of Light and Matter, said Vladimir M. Shalaev, scientific director of nanophotonics at Purdue's Birck Nanotechnology Centerand a distinguished professor of electrical and computer engineering.
"This kickoff workshop will bring together an illustrious group of scientists specializing in diverse areas of quantum physics," he said. "The primary goal is to brainstorm future directions for the field, which will have a profound impact on society in the years to come."
Session chairs and speakers will include senior editors from the journals Science and Nature, researchers from universities including Harvard, MIT, Caltech, UC Berkeley and Columbia, and representatives from federal agencies including the Department of Defense, Air force, Army and Navy.
Speakers will discuss topics in four sessions: Quantum Information and Computing, Quantum Nanophotonics and Metamaterials, Quantum Atomic and Molecular Optics, and Atom-like Solid State Systems.
"Quantum science and technology are likely to bring advances at least as great as those spawned by the integrated circuit and lasers," said Shalaev, who led efforts to create the center along with Chris Greene, Purdue's Albert Overhauser Distinguished Professor of Physics, and Andrew Weiner, the Scifres Family Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
"The next technological revolution will be quantum, and we want to be part of that rather than just observing what's going on," said Shalaev, who is co-director of the center with Greene.
 The potential applications include advanced quantum computers and quantum Internet technology; compact and ultra-precise sensors for a variety of purposes including medical diagnostics and homeland security; and miniature chip-based devices for positioning and navigation instruments with unprecedented precision.
The potential applications include advanced quantum computers and quantum Internet technology; compact and ultra-precise sensors for a variety of purposes including medical diagnostics and homeland security; and miniature chip-based devices for positioning and navigation instruments with unprecedented precision.
Researchers from the College of Science will focus on fundamental research, whereas the College of Engineering is more focused on creating devices based on quantum technology.
The center is an extension of a "pre-eminent team" formed at Purdue in 2013 to work on quantum photonics. Pre-eminent teams are chosen because the work they do has the potential for dramatic impact and international pre-eminence. The colleges of Science and Engineering have hired seven new faculty members in the research area since then.
"One goal of the center is to create a synergistic atmosphere for research in quantum science and technology," Shalaev said.
A group led by Shalaev, Greene and Weiner organized the workshop. A full list of Purdue faculty involved in organizing the workshop is available at http://www.conf.purdue.edu/
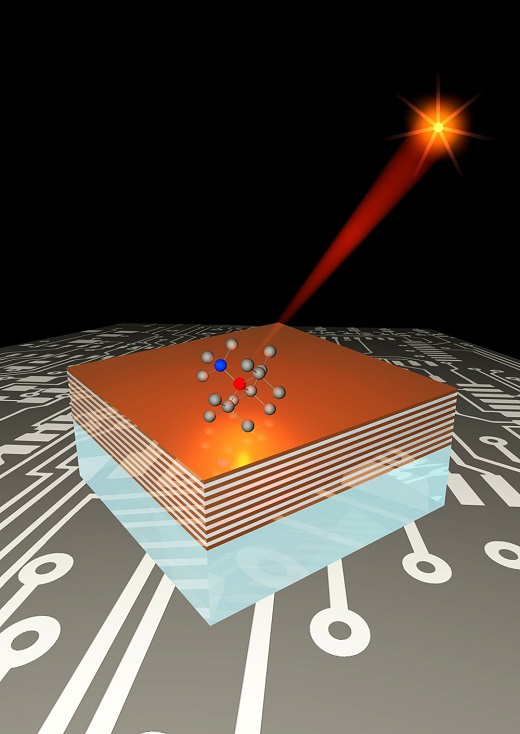
In quantum photonics, technologies could make possible devices that are able to harness single particles called photons, dramatically increasing the performance of computers, sensors and other devices. Conventional computers use electrons to process information. However, the performance might be ramped up considerably by employing the unique quantum properties of electrons and photons.
Quantum computers would take advantage of a phenomenon described by quantum theory called "superposition" or "entanglement." Instead of only the states of one and zero that exist in conventional computers, there are many possible "superposition quantum states." Computers based on quantum physics would have quantum bits, or "qubits," increasing the computer's capacity to process, store and transmit information.
"The challenge is how to keep this very fragile quantum superposition entangled for as long as possible," Shalaev said.
One potential solution is to use lasers to cool atoms nearly to absolute zero in a field known as atomic and molecular optics, or AMO. Another approach is "atom-like solid state systems" harnessing new "metamaterials." Metamaterials are made of engineered structures that contain features, patterns or elements, such as tiny antennas or alternating ultrathin layers of different materials that enable unprecedented control of light. Constructed of artificial atoms and molecules, the optical metamaterials owe their unusual potential to precision engineering on the scale of nanometers.
"Metamaterials could help us control this quantum superposition," Shalaev said.
Quantum technology also could be used to perfect "spintronics." Conventional computers use the presence and absence of an electric charge to represent ones and zeroes in a binary code needed to carry out computations. Spintronics, however, uses the "spin state" of electrons to represent ones and zeros and could bring circuits that resemble biological neurons and synapses to perform tasks such as facial recognition.
"One big challenge for spintronics right now is speed," Shalaev said. "It's too slow. However, we may be able to solve this problem by combining quantum nanophotonics with spintronics to speed it up dramatically."

 How to resolve AdBlock issue?
How to resolve AdBlock issue?